3.4 Right Triangles¶
If a triangle has a right angle, several interesting relationships form. Now that we have similarity defined, we can use it for a second proof of the Pythaogrean Theorem. The area-based proof of the Pythagorean Theorem was shown earlier, but the similarity proof demonstrates the close relationship between the Pythagorean Theorem and the Geometric Mean Theorem.
Theorems¶
If a line segment has as its endpoints the midpoints of two sides of a triangle, then the segment is parallel to and one-half the length of the third side of the triangle.
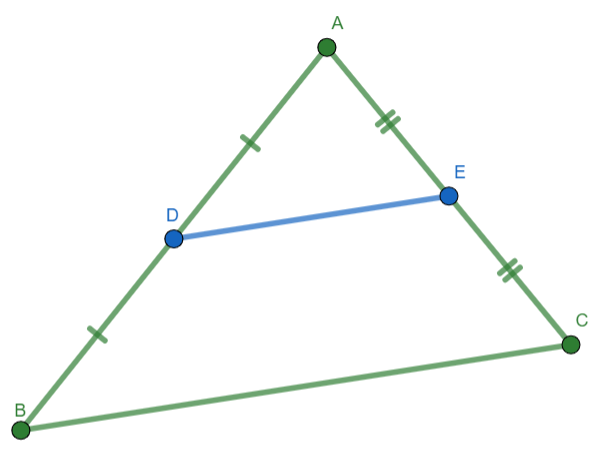
Fig. 12 If \(D,E\) midpoints of \(\overline{AB},\overline{AC}\) respectively, then \(\overline{DE}\parallel\overline{BC}\) and \(DE = \frac{1}{2}BC\).¶
Note
The above theorem has a stunning implication: the midpoints of any quadrilateral are the vertices of a parallelogram. While it doesn’t exactly fit the theme of this section, we’ll prove it here because it is a straightforward consequence of the theorem we just proved.
The midpoints of the sides of a quadrilateral are the vertices of a convex parallelogram.
In a right triangle, the median from the right angle to the hypotenuse is one-half the length of the hypotenuse.
In a right triangle, one of the angles measures \(30^\circ\) if and only if the side opposite this angle is one-half the length of the hypotenuse.
Note
This result along with the Pythagorean Theorem gives us the \(1-2-\sqrt3\) ratio of side lengths for \(30-60-90\) right triangles. The result below about \(45-45-90\) right triangles gives us the \(1-1-\sqrt 2\) ratio of side lenths.
The length of the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle is \(\sqrt2\) times the length of one of its legs.
Hint
Every right triangle has a self-similarity property when an altitude is drawn from the right angle to the hypotenuse. The two smaller triangles created are both similar to the original right triangle. This similarlity property leads directly to a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem.
Pythagorean Theorem (Similarity Proof). If \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the legs of a right triangle the hypotenuse of which has length \(c\), then \(a^2+b^2=c^2\).
